Recognizing Ransomware: Protecting Your Data
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts your files or locks you out of your system, demanding payment (often in cryptocurrency) to restore access. This form of cyber extortion can devastate individuals and organizations, leading to data loss, financial damage, and reputational harm.
How Ransomware Works
Ransomware typically spreads through phishing emails, malicious downloads, or vulnerabilities in software. Once activated, it encrypts files on the infected device, making them inaccessible to the user. The attacker then demands a ransom, usually with a deadline, threatening to delete the files if payment is not made.
Common Types of Ransomware
- Crypto Ransomware: This type encrypts files on the victim’s device, rendering them unusable until a ransom is paid.
- Locker Ransomware: Rather than encrypting files, locker ransomware locks the user out of their device entirely, displaying a ransom note.
- Scareware: This type presents fake warnings about viruses or threats, urging victims to pay for a solution that doesn’t exist.
Signs of a Ransomware Attack
- Unusual File Extensions: If you notice files with unfamiliar extensions or find that your files can’t be opened, it may indicate an infection.
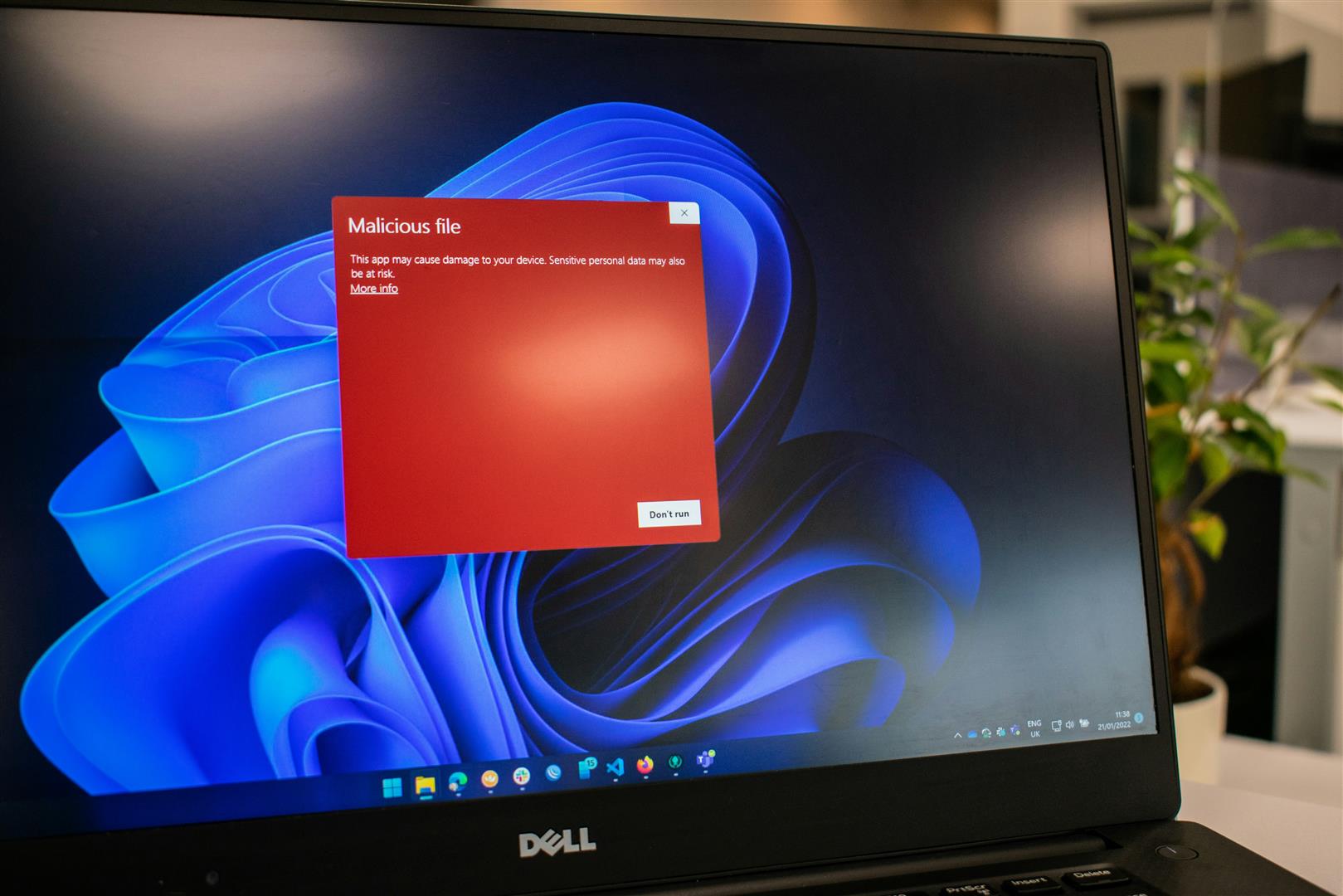
- Ransom Note: A clear sign of ransomware is receiving a ransom note demanding payment in exchange for file access.
- Slow Performance: If your device suddenly becomes sluggish or unresponsive, it could be a sign of malware activity.
Protecting Yourself from Ransomware
- Regular Backups: One of the best defenses against ransomware is to maintain regular backups of your important files. Store backups on external drives or cloud services that are not constantly connected to your network.
- Keep Software Updated: Ensure that your operating system and applications are up-to-date. Regular updates patch vulnerabilities that ransomware often exploits.
- Use Antivirus Software: Install reputable antivirus software that provides real-time protection against ransomware and other malware.
- Be Cautious with Emails and Links: Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources. Phishing emails are a common way ransomware is delivered.
- Implement Network Security Measures: For businesses, implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and segmentation can help protect against ransomware attacks.
What to Do If Infected
If you suspect a ransomware infection, take immediate action:
- Disconnect from the Network: Isolate the infected device from your network to prevent the ransomware from spreading.
- Do Not Pay the Ransom: Paying the ransom does not guarantee that you will regain access to your files and may encourage further attacks.
- Report the Incident: Report the attack to law enforcement and relevant cybersecurity authorities. They may be able to provide assistance.
- Restore from Backups: If you have backups available, restore your files from them after ensuring the malware has been removed.
Conclusion
Ransomware poses a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike. Understanding how it works and recognizing the signs of an attack are crucial for effective prevention. By implementing strong security measures, maintaining regular backups, and staying informed about cyber threats, you can safeguard your data against ransomware attacks.